Last Updated on May 30, 2025
The importance of teaching language and content together to support ELD instruction is one of the “Big Ideas” woven through the WIDA English Language Development Standards Framework, 2020. The California English Language Development Standards also promote the practice of teaching language and content together in both designated and integrated language instruction.
As the WIDA framework explains, “multilingual learners develop content and language concurrently, with academic content as a context for language learning and language as a means for learning academic content.” (WIDA ELD Standards Framework 2020, p. 19).
Multimedia resources with instructional scaffolds and differentiation strategies, such as those on the Listenwise platform, support teaching language and content together. In this blog post, we’ll share the experience of an elementary school teacher who uses Listenwise to support integrated ELD instruction.
In this blog post, we’ll share the experience of an elementary school teacher who uses Listenwise to support integrated ELD instruction.
Using Listenwise to Support Integrated ELD Instruction
Gretchen Hummon teaches 5th grade at Crocker Elementary in Fitchburg, MA. She has students at a variety of levels of English language proficiency in her general education classroom, including 8 students who are designated English language learners, mostly native Spanish speakers. There is an ELD teacher who both pulls students out for designated language instruction and pushes into the classroom for support during integrated instruction.
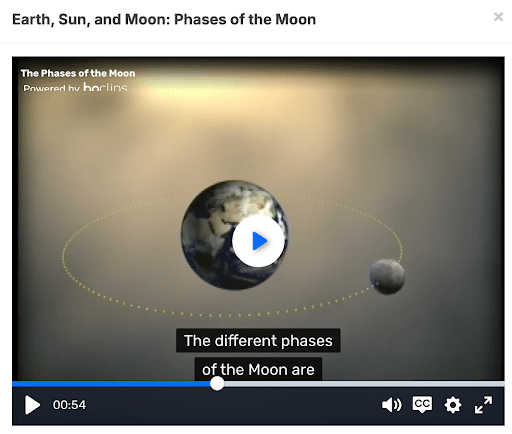
Gretchen’s class was studying the phases of the moon as part of the Mystery Science curriculum. She incorporated a Listenwise podcast lesson on the Phases of the Moon into the unit before doing a hands-on activity using flashlights to simulate the moon’s orbit. She adapted instructional activities from the teacher’s guide for before, during, and after listening to fit into her own routines and curriculum.
Before Listening – Building Background Knowledge
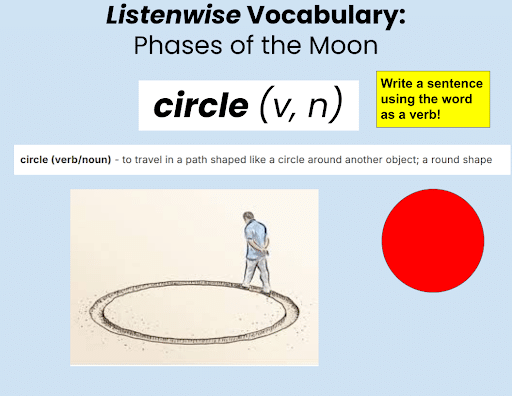
First, Gretchen activated students’ prior knowledge by asking what they knew about the moon. Then she introduced several vocabulary words featured in the podcast, which were selected because they are important to understanding key concepts and are used frequently across contexts. She noted that several words students may have known as nouns were used in the podcast as verbs (e.g., circle, inch, shadow). For each word, she asked if students recognized it as a Spanish cognate.

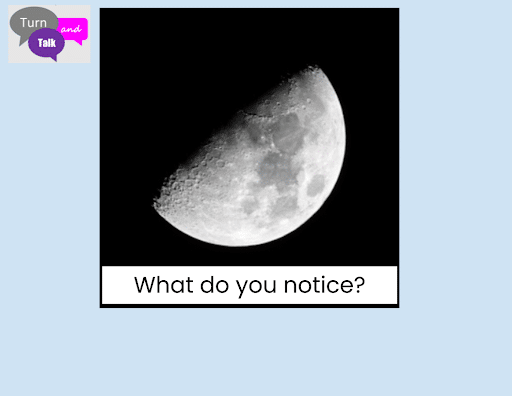
Next, she showed students images from the Listenwise lesson and asked students to turn and talk about what they noticed. Then she showed a short video illustrating the phases of the moon and asked students additional questions about it. The use of visuals and brief conversations helped students build background knowledge to further prepare them to listen to the podcast.
During Listening – Providing Learning Supports
Gretchen asked her students to listen to the 2-minute “Phases of the Moon” podcast twice. The first time, she played the podcast for the class and asked students to listen while reading the interactive transcript that follows along with the audio on the screen.
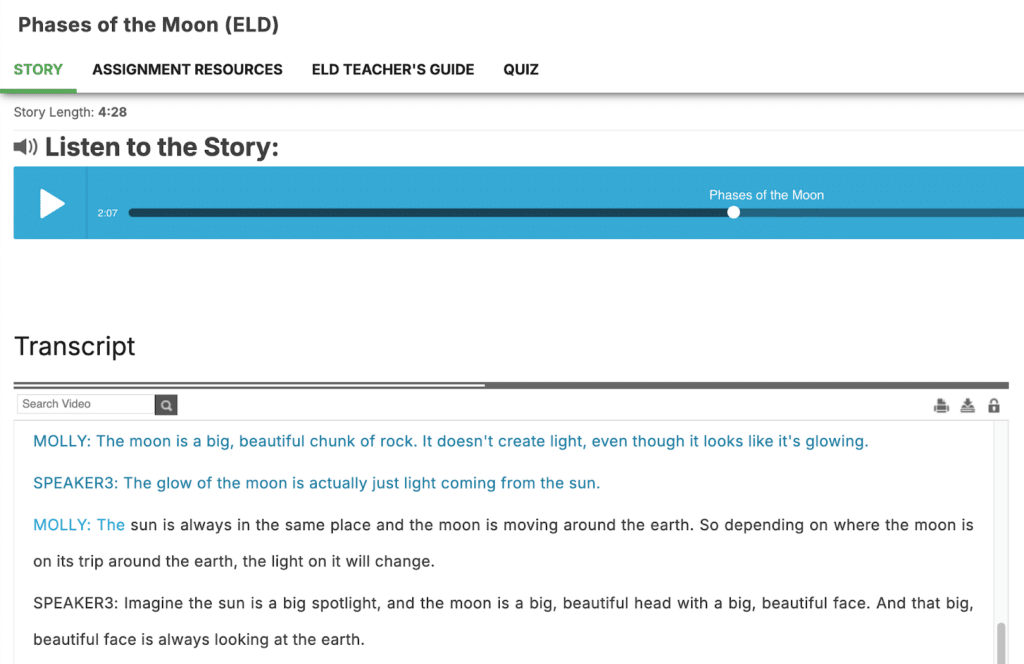
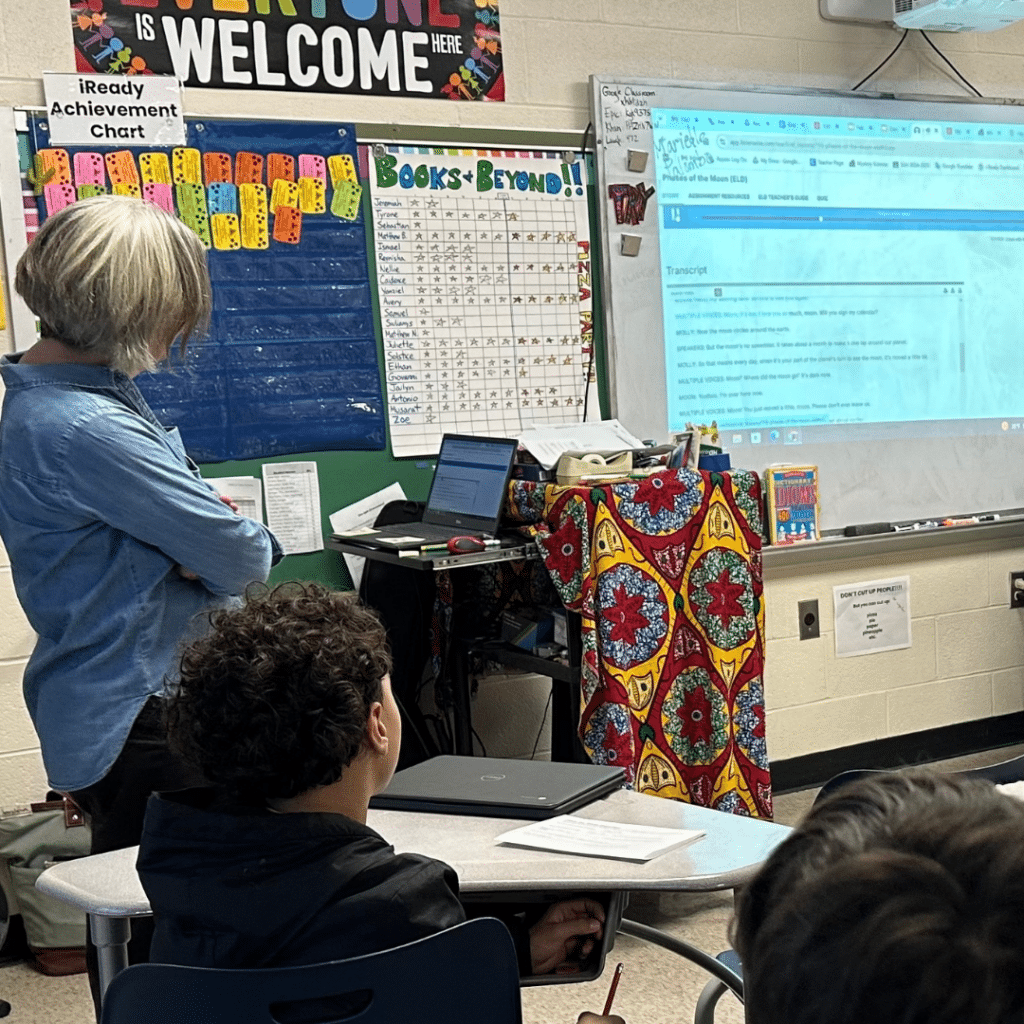
During the second listen, she asked students to fill in the blanks in sentences excerpted from the podcast on a printed worksheet. She stopped the audio after students heard each sentence to allow them time to fill in the missing word. This helped to focus their listening, and also provided notes to use during the activities that followed.
After Listening – Deepening Learning Across Language Domains
After students had listened to the podcast twice, Gretchen asked them to write responses to the open-ended comprehension questions printed on the other side of the worksheet. She said they should try their best, even if they were unsure of the answers, because that would help her to know what they understood so far and what might need more clarification. She translated each question into Spanish (which was read aloud by Google Translate), and one student who was a beginning English language learner wrote his responses in Spanish.
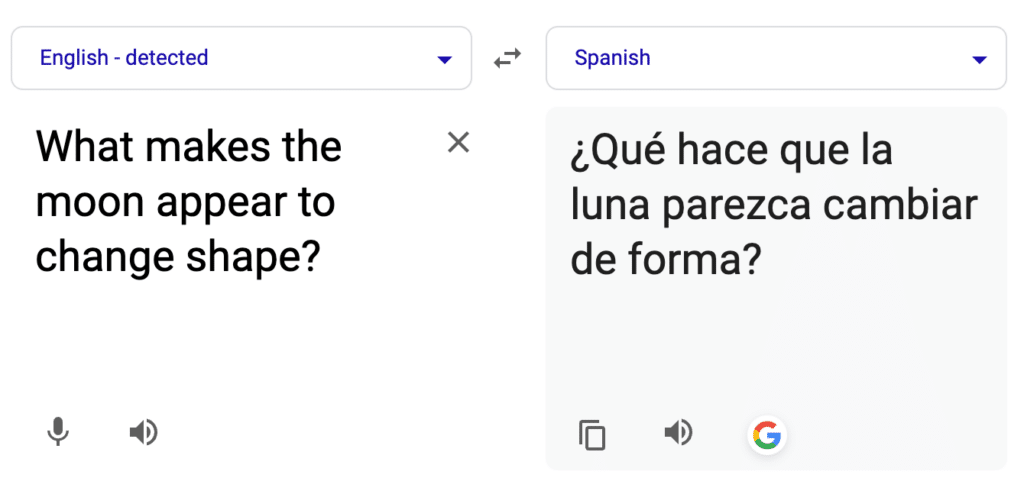
Once students had written their responses, the class discussed them. Gretchen invited students to share their answers orally and recognized when they used academic vocabulary appropriately in context. Through writing and speaking, students were able to practice academic language while also deepening their understanding of science.
Newcomer Support with Lingolift
During independent work time, the beginner ELP level student practiced speaking with Lingolift, a companion to Listenwise for newcomers. He followed the Watch, Learn, Speak sequence for a collection of short videos focused on the topic of space and practiced writing words and speaking sentences from the video to build vocabulary and practice fluency and pronunciation.